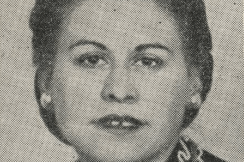Era: New Boston(~1950-1995)
Urban renewal, the taking, Government Center, Charles River Park, highways, bussing
While the demolition of the West End began in 1958, the momentum for its destruction and for the federal urban renewal program itself began 20 years earlier, in the aftermath of the Great Depression. The Housing Act of 1949 would later mark the official birth of the federal Urban Renewal Program. Although it aimed to revitalize struggling inner cities, it often did so at the expense of established communities and displaced residents.
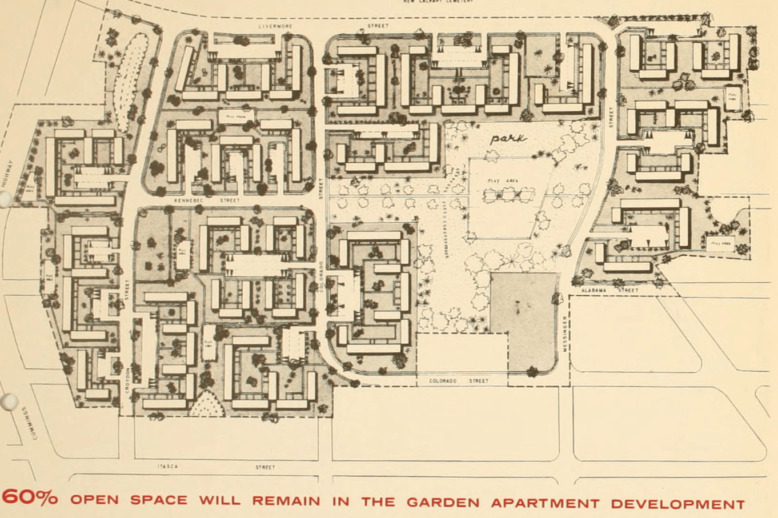
The Mattapan Project was first mentioned by the Boston Housing Authority in 1952 and later by the Boston Redevelopment Authority in 1962 as a possible urban renewal project. Despite the preliminary planning funding being granted in 1963 and the urban renewal application prepared in 1964, the project was dropped by the City of Boston. The delays in the Mattapan Project’s site development and the eventual abandonment of the plan helps to demonstrate the changes in public opinion on urban renewal projects of the time.
The Lost Streets of the West End: Minot Street was one of the dozens of narrow, residential, West End streets razed by redevelopment in the 1950s. While the two street blocks on the northern side of the redevelopment zone were changed profoundly by urban renewal, the site’s rich history represents the constantly shifting geography of the Boston cityscape over the past two centuries.
Charles River Park is an apartment complex built on 45 acres of the historic West End, soon after its demolition. Jerome Rappaport, Sr., attorney for Charles River Park, Inc. and one of the corporation’s early investors, was politically connected to Mayor John Hynes, whose platform for a “New Boston” was the pretext for urban renewal. The vast majority of West Enders could not afford the luxury apartments that replaced their homes. The first tenants of Charles River Park were offered many modern, communal amenities – intended to attract young professionals and suburban families alike.
Richie Nedd was one of the historic West End’s Black residents and a board member of The West End Museum before his passing in 2011. Nedd’s article for the June 1998 issue of The West Ender, “A Black Man’s View of the West End,” features he and other Black residents coming together in reunions of hundreds of West Enders after urban renewal.
Joseph “Bepo” Caruso came to the West End from Sicily when he was seven years old. During his rich life he served in World War II, opened an art gallery, published novels, started a film production company, and was a founder of the Committee to Save the West End.
One of the few independent female lawyers of her day, and a staunch supporter of her community, Gladys Shapiro became one of the most influential women to emerge from the West End.
John Moore understood himself to be a West Ender when he grew up on Grove Street on the north slope of present-day Beacon Hill. The demolition of fifty acres of the historic West End and the preservation of the Beacon Hill Architectural District were simultaneous, influencing popular perceptions of the boundaries not just of Boston’s contemporary neighborhoods, but its historic ones as well.