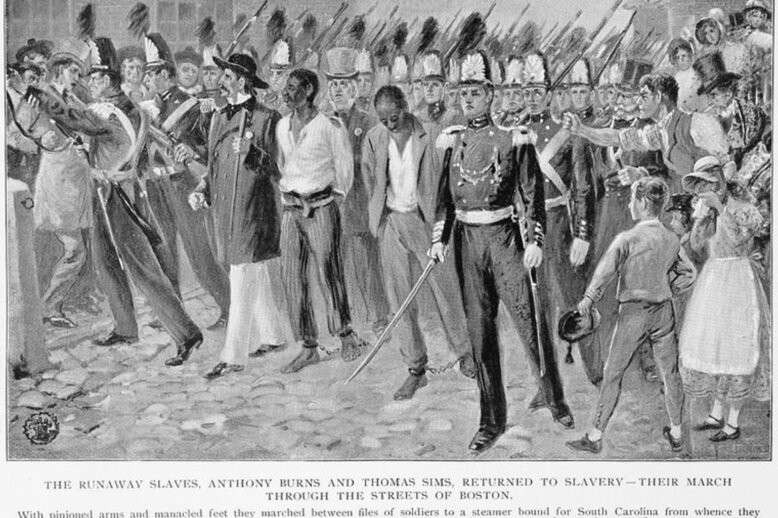
The Fugitive Slave Laws in Boston: Part 2, 1850–1855
The Fugitive Slave Laws in Boston: Part 2, 1850–1855 This article, part 2 in a series on fugitive slaves in Boston, explores the new legislation passed during the lead up to the Civil War which expanded the reach of the fugitive slave law, and the reactions of Bostonians to slave catchers targeting residents. Part 2…