Era: Immigrant Neighborhood (~1880-1960)
Immigration, first, second, and third-generation Americans, Settlement Houses, Irish politics, etc.
The West End News: The Editor and the PublisherOne Summer in the West End, Part One Over the course of four months in the summer of 1926, Lou Coffee and Francis R. Whelton published a newspaper by West Enders for West Enders. These papers offer a glimpse into a diverse immigrant neighborhood facing the introduction…
Edmund L. Mitchell: Photographer of a Changing Boston With over 5,700 photographs, the Edmund L. Mitchell Collection, now housed at the Boston Public Library, offers a snapshot of Boston and the West End in a period of transition. As an amateur photographer, Mitchell nonetheless captured the city as it became something new. Edmund Lombard Mitchell…
The West End Branch of the Boston Public Library Library service in the West End neighborhood began in 1896 in the Old West Church on the corner of Cambridge and Lynde Streets. The branch remained there until 1960 when the West End Redevelopment Project forced its closure. In 1968 the current library building opened at…
The Greatest Political Enemies of the 20th Century: West End’s Lomasney Vs. Mayor Curley In the early decades of the 20th century, two towering figures dominated Boston’s political landscape. Their rivalry was so bitter that it reshaped the very nature of urban Democratic politics. The feud between Martin Lomasney, the “Mahatma” of the West End,…
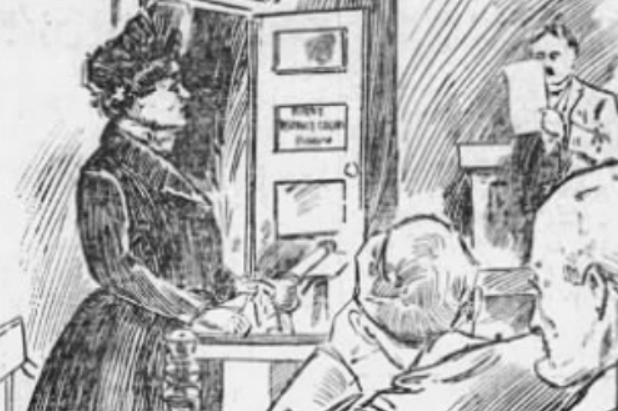
Jolly Jane Toppan: The MGH Nurse Turned Mass Murderer A medical serial killer in the late 19th and early 20th century, Jane Toppan (1857-1938) admitted to the murders of 31 people and was possibly responsible for many more deaths. Toppan, a child of Irish immigrants and a trained nurse, was a press sensation in her…
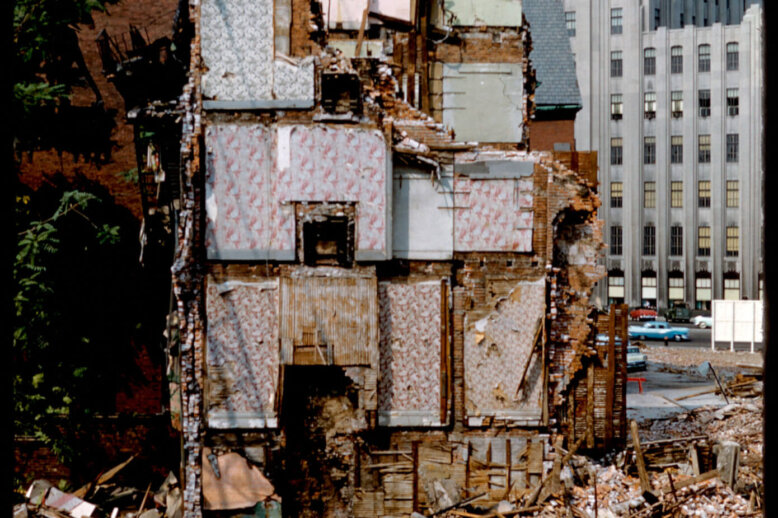
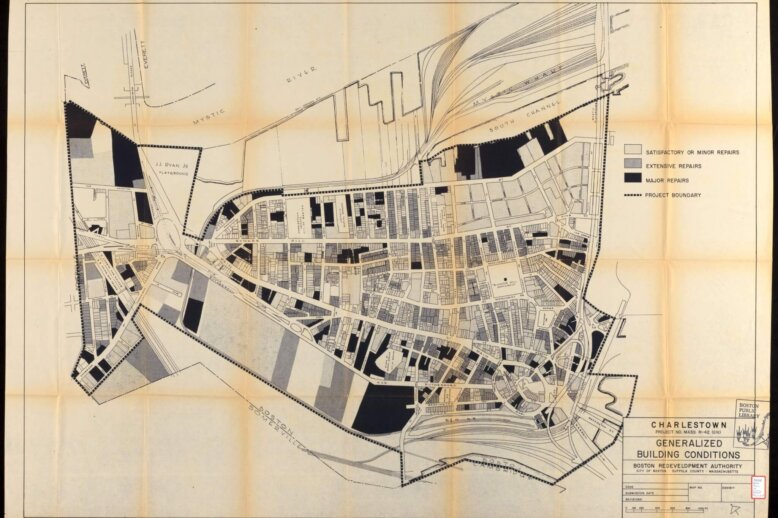
Boston’s urban landscape has been dramatically shaped by urban renewal initiatives of the mid-20th century. Among the most notable examples are the West End and Charlestown—two historic neighborhoods with starkly divergent urban renewal results. While the West End became the poster child for urban renewal’s destructive potential, Charlestown had a very different outcome only a few years later. This article examines these contrasting urban renewal experiences, highlighting their implementation approaches, community responses, and lasting impacts on Boston’s urban fabric.
At its peak, the vibrant West End neighborhood was home to approximately 40-45 synagogues, reflecting the thriving Jewish community that once defined the area. Today, only the Boston Synagogue remains as the sole continuously-operating Jewish house of worship in the neighborhood.
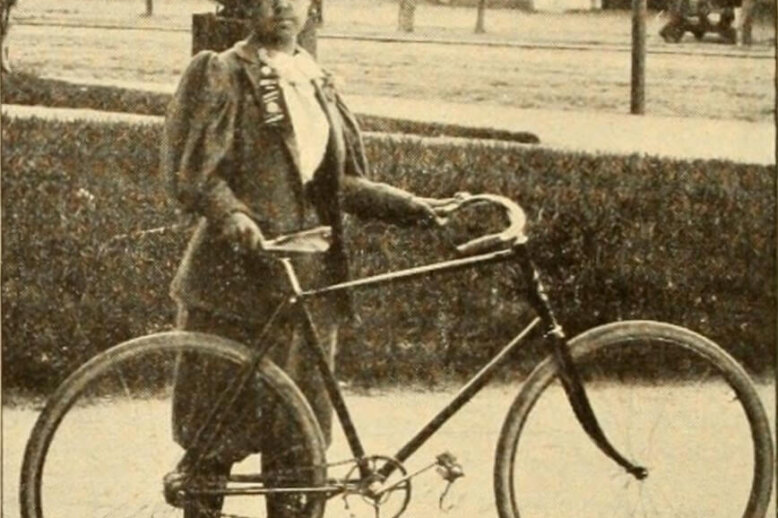
Below is an online, self-guided version of our “West End Women” walking tour. Print it out or keep it digital, and put on your best walking shoes to explore the histories and stories of women from Boston’s West End.