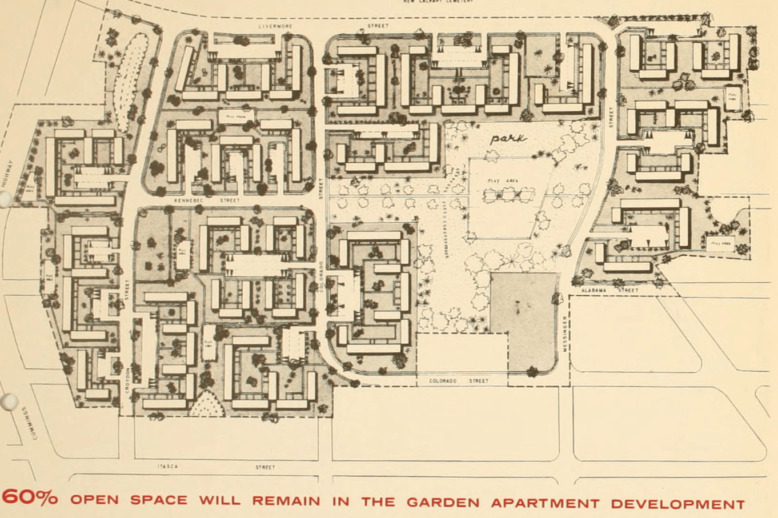
Rid of the Grid: The Destructive Legacy of Superblocks in Urban Renewal
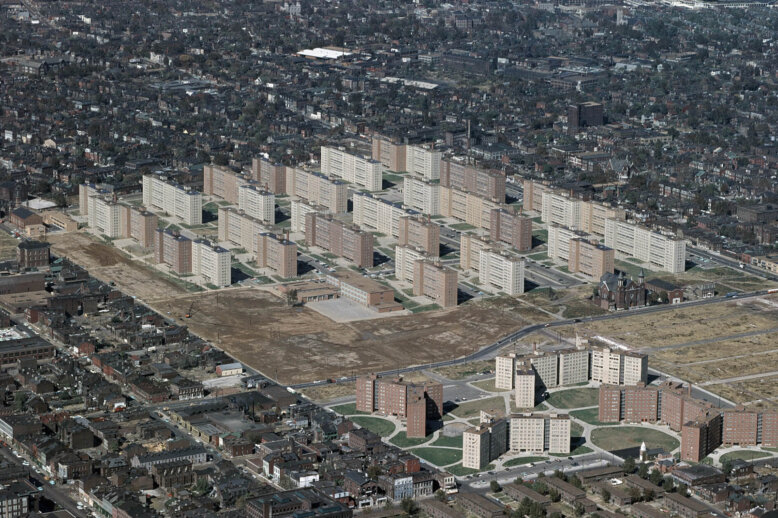
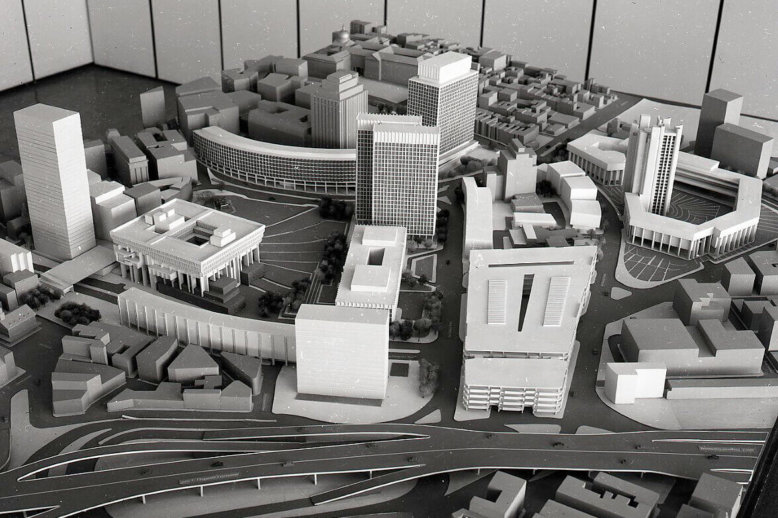
In the 20th century, the superblock concept emerged from modernist planning principles as an alternative to the traditional grid. These superblocks, while theoretically promising a more ordered and healthy urban environment, proved destructive when implemented through America’s urban renewal programs, including in Boston’s West End.