Topic: Art & Literature
Art, fine arts, artists, books, film, authors, actors, other creative forms
Bernard Berenson (1865-1959) was a Lithuanian-born, West-End-raised art historian and commercial art dealer specializing in the Italian Renaissance. His knowledge and expert connoisseurship greatly impacted the art world of the 19th and 20th centuries, and his dealings with wealthy Americans bolstered the flow of Old Masters into the country. His publications on Italian Renaissance artists were hugely successful and are still used in classrooms today.
Entrepreneur Christiana Carteaux Bannister and artist Edward Mitchell Bannister married in Boston’s West End in 1857. Throughout the 1850s and 1860s, they were active in Boston’s abolitionist and artistic communities. During these years and beyond, their symbiotic financial and creative partnership helped to bolster both of their careers and their community connections.
Settlement houses were a valuable resource for immigrant families, providing them educational and health services, and practical support in adapting to their new country. Some settlement houses offered specialized services, such as music school settlements, which gave children and adults an opportunity to escape the daily struggles of city life by engaging with the arts.
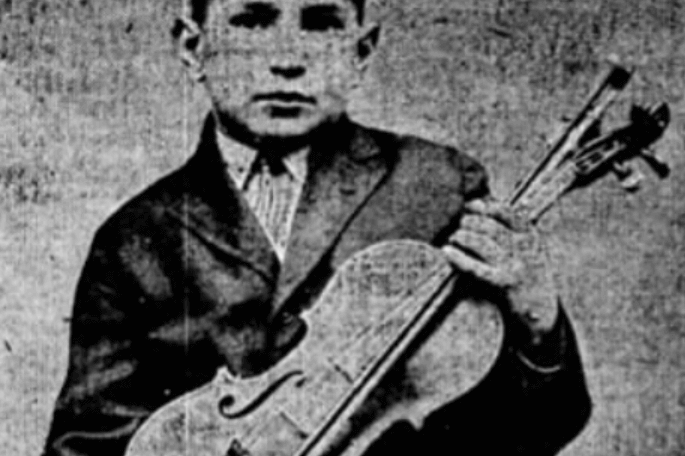
Joseph D. Portanova was the child of Italian immigrants who settled in the West End. He was introduced to art by Eva Whiting White at the Elizabeth Peabody House and went on to become a prolific, nationally known sculptor.
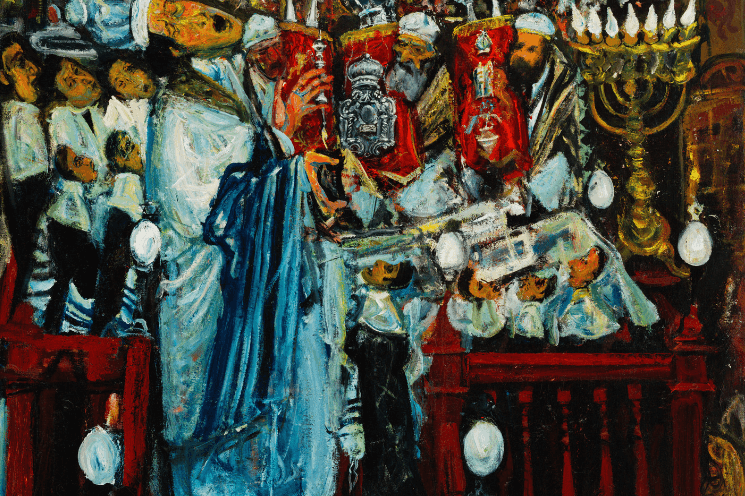
Born into an Orthodox Jewish family, artist Hyman Bloom grew up in the West End attending the Vilna Shul with his father. In adulthood, he veered away from Orthodox Judaism and towards the mystic, esoteric, and occult. Bloom’s art both parallels and is the product of his spiritual journey.
Like many fellow West Enders of her day, Dorothy Pastore relished an afternoon escape to the Lancaster Theater. There, neighborhood children from diverse backgrounds would join together and enjoy a break from the stresses of school and everyday life. Such experiences reinforced the notion of the West End as an urban village.
Hyman Bloom is remembered as a key figure from the Boston Expressionist movement, praised for his mystical and vibrant paintings. Bloom, in addition to being a visionary artist, offers us a window into Boston’s settlement houses in the 1920s and ‘30s. The West End Community Center, and its artist-teacher Harold Zimmerman, nurtured the creativity of a generation of future artists, from Bloom to Jack Levine.
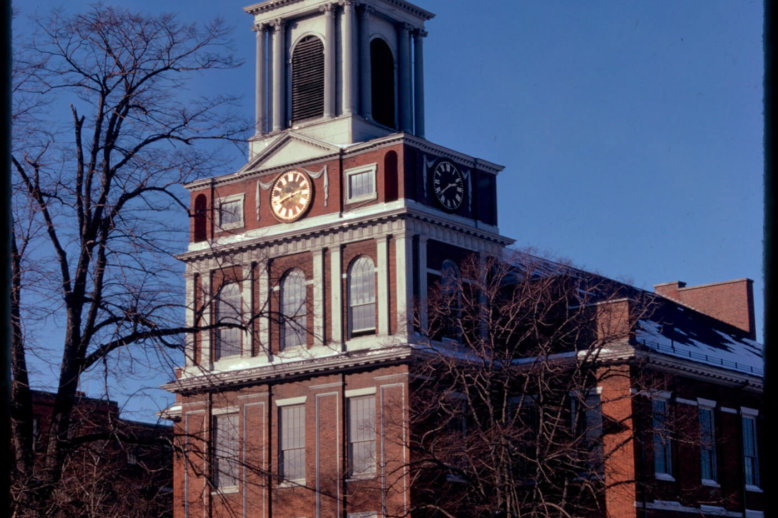
The Old West Church, standing at 131 Cambridge St, is one of the few surviving buildings of the historic West End. Since its opening in 1806, the building has served as a church, a library, a shelter, and a church again. It continues to hold masses and contribute to the Boston community today.